🔖 Introduction
About the project
Log2AI is an advanced Multi-Agent RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) system designed to transform chaotic application logs into actionable intelligence. Built for high-traffic healthcare systems (HealthHub), the goal was to eliminate the manual "needle-in-a-haystack" search during system outages.
I developed a sophisticated pipeline that ingest JSON logs, intelligently chunks them by session/request ID, and stores them in a PostgreSQL vector database (pgvector). By implementing a multi-agent architecture (Retrieval, Summarization, and Verification), I enabled DevOps teams to ask natural language questions like "What caused the payment failures on the 13th?" and receive verified, streaming answers in seconds. The result was a 25x increase in analysis speed compared to traditional manual log searching.
🤔 Problem space
Problems to solve/Requirements to Create
The central challenge was the High-Stakes Observability required in healthcare. When a system slows down or a patient record isn't loading, every second counts.
👉 Problem: The "Technical Barrier" to System Insights
In modern DevOps, analyzing system health requires "Log Experts" who are proficient in complex query languages like SQL, Lucene (ELK), or KQL (Azure).
The Issue: Non-technical stakeholders (Compliance Officers, Tech Managers) or even busy On-Call engineers cannot simply "ask" the system a question. They are bottlenecked by specialized syntax, turning a 10-second question into a 20-minute manual search.
Current solution: DevOps teams build static, pre-defined dashboards. If a problem occurs that hasn't been "pre-built" into a dashboard, engineers must fall back to manual terminal grep commands.
How do we know it is a problem: Industry Metric: High MTTR (Mean Time to Resolution). Only senior engineers hold the "tribal knowledge" to find specific traces, creating a single point of failure during outages.
👉 Requirement: The "Signal vs. Noise" Crisis in Healthcare Compliance
Healthcare regulations (like HIPAA) mandate that every interaction—even successful ones—must be logged (INFO logs). This creates a "Data Haystack."
The Issue: 99% of logs are "Normal Activity" (User viewing a record, Lab results generated). These are critical for audits but act as "noise" that buries the 1% of critical system errors. Traditional tools treat all logs with equal weight, making it impossible to quickly isolate the "story" of a failure among millions of successful events.
Current solution Engineers often "filter out" INFO logs to make searching faster, but this destroys the audit trail. Alternatively, they pay massive costs for high-volume indexing in tools like Splunk or Datadog.
How do we know it is a problem
Why solve these problems?
It is critical to address these problems now because, in the healthcare industry, system downtime and data security are not just technical issues—they are matters of patient care and legal liability.
Reason: Reducing "Log-Analysis Tax": High-salary senior engineers currently spend ~30% of their time manually "detecting" errors. By automating this, the company shifts its most expensive human resources from "maintenance" to "feature innovation."
Reason: Eliminating Compliance Blind spots: Manual audits are prone to human error. An AI-driven system ensures that no user activity trace is missed, significantly reducing the risk of multi-million dollar regulatory fines.
Reason: Democratizing Data: By removing the "Technical Barrier," we empower non-technical staff to perform their own investigations, removing the bottleneck on the DevOps team.
Goals
Company objective 🎯
To achieve "Zero-Friction Observability"—reducing Mean Time to Repair (MTTR) and ensuring 100% compliance transparency by empowering any team member to audit and debug system activity using natural language.
Project goals
Enable Natural Language "System Chat" (Aligns with Problem: Technical Barrier) To eliminate the need for complex query syntax (SQL/Grep) by implementing a high-performance semantic search database (pgvector). The objective is to allow anyone—regardless of technical background—to find system insights through simple conversation.
Implement "Intelligent Signal Isolation" (Aligns with Problem: Signal vs. Noise) To architect a custom ingestion pipeline that automatically groups millions of fragmented logs by request_id. This ensures that mandatory compliance INFO logs act as a rich context for the story, rather than "noise" that buries critical errors.
Engineer a Hallucination-Free Verification Engine (Aligns with Problem: Trust-But-Verify Requirement) To develop a Multi-Agent architecture where a dedicated Verification Agent cross-references every AI claim against raw log snippets. This ensures that the system provides only fact-grounded, audit-ready sightings, meeting the rigorous trust standards of the healthcare industry.
User Stories
User type: On-Call DevOps Engineer
The "first responder" during system outages or performance degradation. They are responsible for troubleshooting and restoring high-availability healthcare services as quickly as possible.
Goals: Minimize the Mean Time to Repair (MTTR) by identifying the exact root cause of a system failure (e.g., a failing payment gateway or a database timeout) in seconds rather than minutes.
Needs: A natural language interface to "ask" the logs about specific errors, and a system that automatically reconstructs the full "transactional story" by linking related log events across disparate services.
Other characteristic: Highly technical but operates under extreme pressure; requires verified log snippets from the AI to maintain trust in the automated analysis.
🌟 Design space
UI Design
The UI for Log2AI was designed with a "Command Center" philosophy. Since the primary users are engineers working under high-pressure outage scenarios, the interface prioritizes clarity, speed, and real-time feedback.
The Launchpad: Users arrive at a clean, dark-themed dashboard that emphasizes a central search bar.
The Inquiry: Users type natural language questions (e.g., "What caused the lab record failure on 2026-01-17?").
The Agentic Stream: As the Multi-Agent system works, a real-time stream appears. Users don't just see a final answer; they see the system searching, retrieving context, and verifying facts.
The Resolution: The final verified answer is presented with cited log snippets and a clear "Audit Trail," allowing for immediate debugging action.
Low-fidelity Wireframe

The "Focus-First" UI
The core concept was to merge a standard Chat interface with a technical "Log Feed."
Floating Input: The input area is anchored at the bottom (Standard Chat UX), allowing the rest of the screen to serve as a high-visibility canvas for the log analysis stream.
High-fidelity design
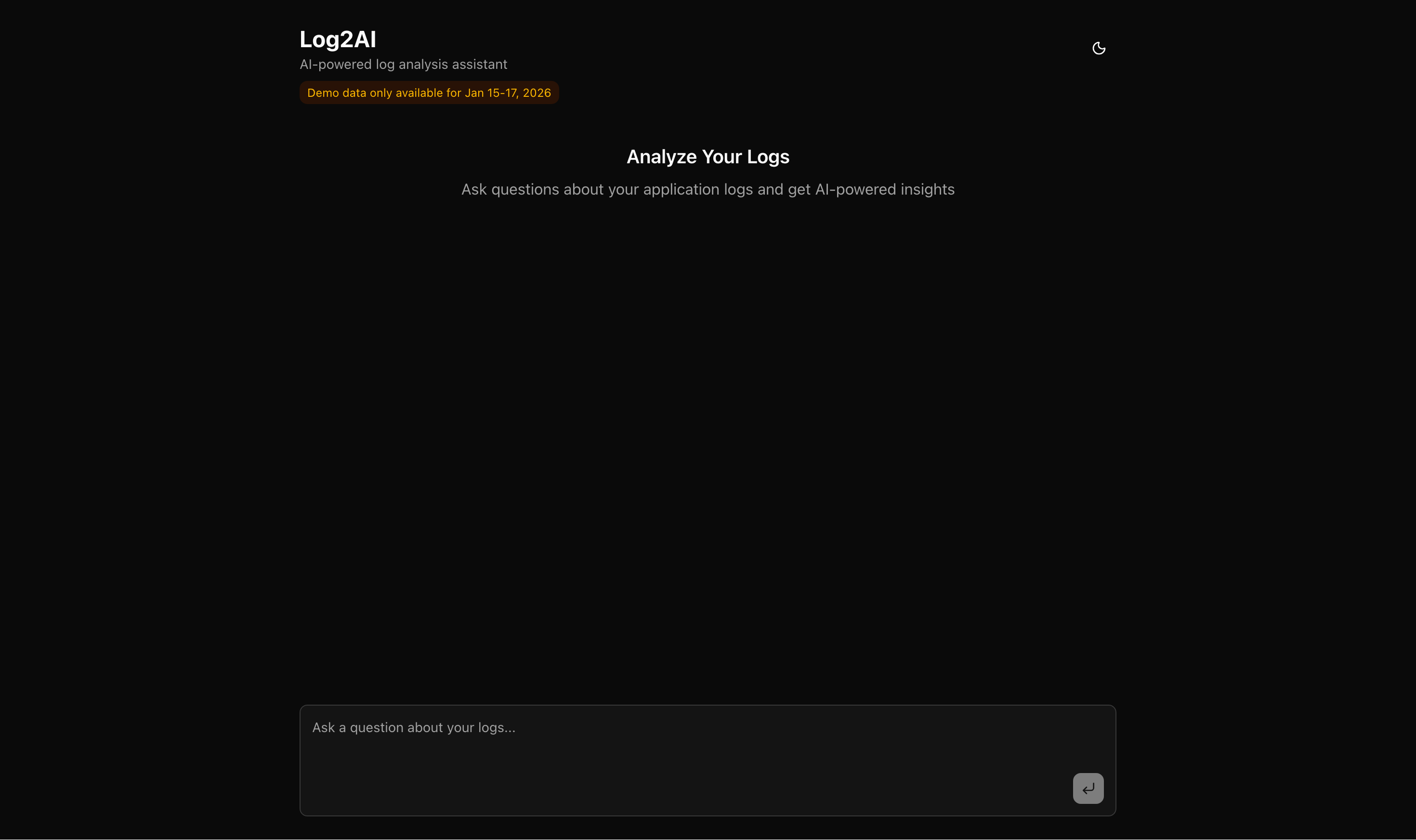
The high-fidelity design realizes the "Command Center" vision with a premium, minimalist aesthetic that feels both modern and professional. By utilizing a deep obsidian background and high-contrast typography, the interface ensures maximum readability for technical data.
Key Design Elements:
Minimalist Hero Section: The center of the screen is dedicated to the primary action: "Analyze Your Logs". By keeping the initial state clean, we reduce cognitive load for users who are already under pressure.
Anchored Chat Interface: The query area is anchored at the bottom with a subtle glassmorphism effect. This familiar "Chat UX" makes the advanced Multi-Agent backend feel approachable and easy to use.
Dynamic Theme Engine: A seamless theme-switching system allows users to toggle between a focused dark mode—ideal for late-night debugging—and a high-clarity light mode for daytime audits.
Design system 🎨
For the Log2AI frontend, I implemented the shadcn/ui design system, built on top of Tailwind CSS and Radix UI.
Why a Design System was Necessary: In a high-stakes industry like Health-Tech, the interface must communicate reliability and precision. Developing a custom UI kit from scratch would have been time-consuming and prone to visual inconsistencies. By utilizing a proven design system, I could ensure that every button, input, and modal followed a unified design language, giving the tool a "production-ready" feel from day one.
How I Utilized it:
Accessible Components: I used Radix-based primitives (like accessible Dialogs and Popovers) to ensure that the tool remains usable for all stakeholders, including those using screen readers—a critical requirement for enterprise healthcare software.
Rapid Prototyping: The modular nature of shadcn allowed me to focus 90% of my development time on the complex streaming logic and Multi-Agent state management, rather than worrying about CSS-in-JS or component styling.
Development Phase
Technology Stack Selection
The tech stack for Log2AI was carefully chosen to balance high-performance data processing with cutting-edge AI orchestration.
1. Backend - FastAPI (Python)
Why FastAPI?
Asynchronous Excellence: Logs can be massive. FastAPI’s async/await support allowed me to handle streaming responses (SSE) and heavy database I/O without blocking the main thread.
Native AI Integration: Python is the lingua franca of AI. FastAPI provides the most robust environment for integrating LangChain, Google Gemini, and Pydantic-based data validation.
Built-in Documentation: Auto-generated Swagger/OpenAPI docs made it effortless to test the complex /sync and /qa endpoints.
2. AI Orchestration - LangGraph
Why LangGraph?
Stateful Multi-Agent Workflows: Unlike standard linear chains, LangGraph allowed me to build a cyclic graph where agents can loop back and verify information.
Precision Routing: It provided the granular control needed to route questions between the "Retrieval Agent" (to find logs) and the "Verification Agent" (to check for hallucinations).
Persistence: Using LangGraph’s MemorySaver, I implemented conversation history, allowing the AI to remember context like "Show me the logs for the 13th" in follow-up questions.
3.Vector Database - PostgreSQL with pgvector (Supabase)
Why pgvector?
Enterprise Reliability: I chose PostgreSQL over niche vector databases because it is a battle-tested, relational engine. pgvector adds high-performance semantic search directly into the database.
Hybrid Queries: It allows me to combine Vector Search (similarity) with Metadata Filtering (e.g., searching only for logs from lab_id: 42), which is essential for healthcare audits.
4. Frontend - Next.js with Tailwind CSS & shadcn/ui
Why this stack?
Server-Side Streaming: Next.js handles Server-Sent Events (SSE) beautifully, enabling the "Live Thinking" stream from the AI agents.
Developer Velocity: Tailwind and shadcn/ui allowed me to create a premium "Command Center" aesthetic in a fraction of the time, ensuring the interface was as modern as the backend.
5. Streaming Interface - Vercel AI SDK
Why the Vercel AI SDK?
Seamless Streaming: It abstracts the complexity of handling Server-Sent Events (SSE). It allowed me to implement the "Typewriter effect" and the "Live Thinking" stream with just a few lines of code.
State Management: The SDK's useChat hook automatically managed the conversation state, message history, and loading indicators, ensuring a smooth and responsive user experience.
Interoperability: By building a backend compatible with the Vercel AI SDK, I ensured that the Log2AI core can be easily integrated into any modern React or Next.js application in the future.
High-Level Architecture Diagram
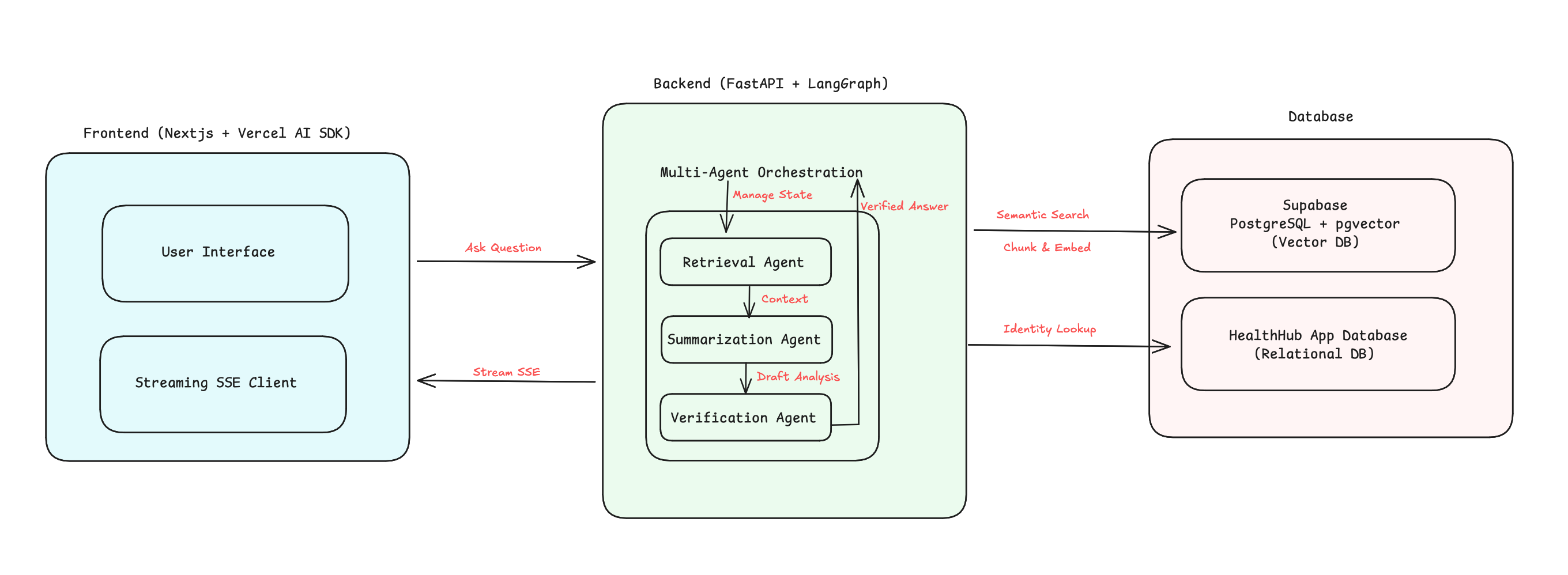
I designed the system using a Multi-Agent RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) architecture. This modular approach separates log ingestion from intelligent analysis, ensuring scalability and high precision.
Architecture Highlights:
Stateful Graph Orchestration: I utilized LangGraph to manage the state of the conversation. This allows the system to support multi-turn dialogues where the AI remembers previous context (e.g., resolving "What about the 13th?" based on a prior request).
Asynchronous Ingestion Pipeline: The Log Sync Engine performs request-based chunking and generates vector embeddings in parallel, ensuring that millions of logs are indexed into pgvector with high efficiency.
Agentic Cross-Verification: To meet healthcare industry standards for accuracy, the Summarization Agent's output is reviewed by a Verification Agent. This agent's only job is to cross-check claims against raw log data, effectively neutralizing AI hallucinations.
Interoperable Streaming: The system communicates via Server-Sent Events (SSE) using a format compatible with the Vercel AI SDK, allowing for a responsive, "live thinking" user experience.
Entity-Extended Relationship Diagram or Class Diagram or Any other Detailed Diagrams
Detailed Data Architecture: Request-Centric Schema
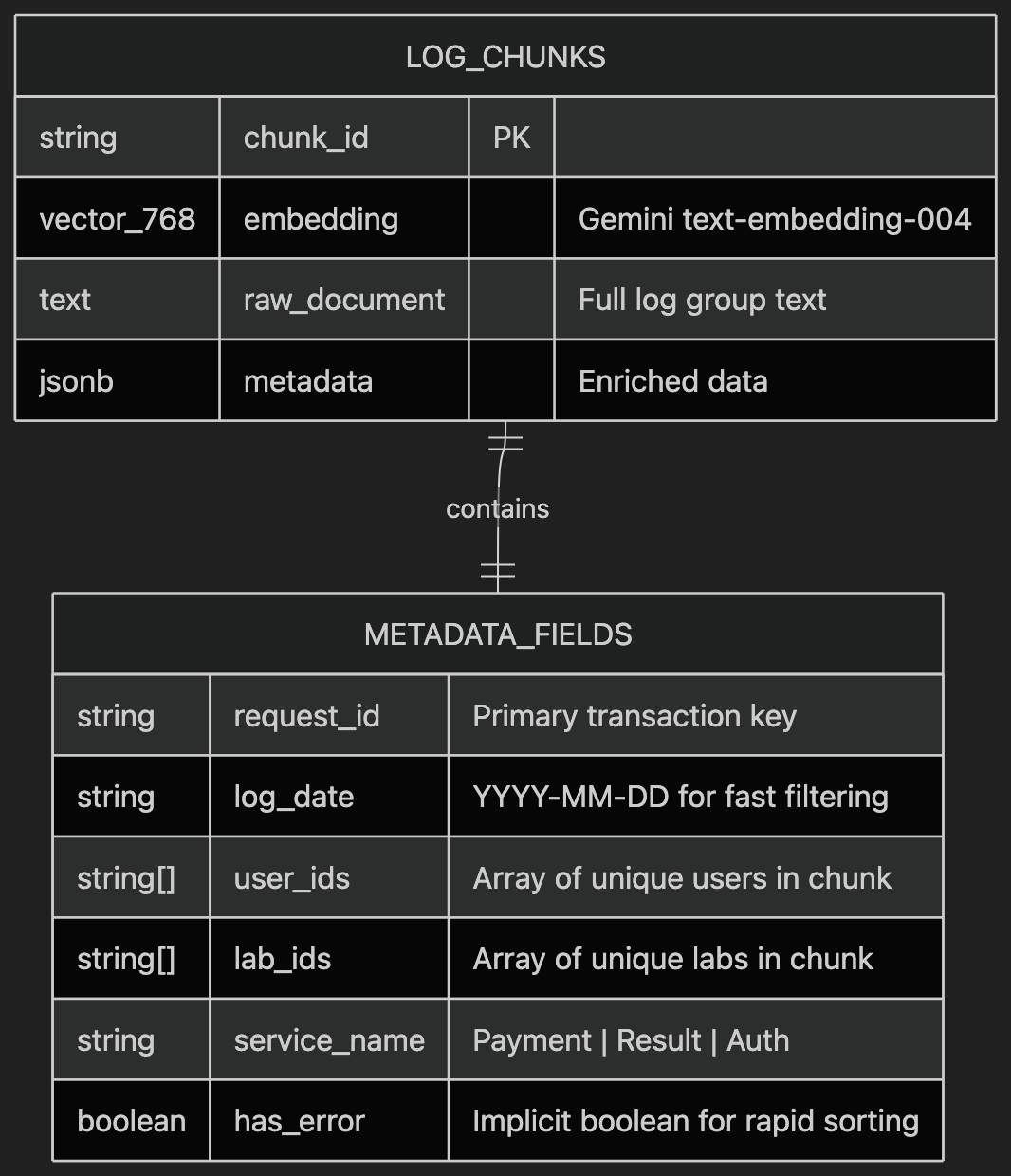
A critical architectural decision in Log2AI was the design of a specialized log schema. Unlike traditional log search tools that treat every line as an isolated event, my schema is designed for Transactional Traceability.
The Hybrid Chunking Strategy: To provide the AI with the best context, I implemented a hybrid chunking strategy during ingestion:
Request-Grouped Chunks: Logs sharing the same request_id are grouped together, capturing the complete "story" of a user's transaction.
Size-Aware Splitting: If a single request generates over 100 log lines, it is intelligently split into 10-minute windows to maintain high embedding precision.
Semantic Metadata Enhancement: Every chunk is enriched with user IDs, lab IDs, and service names, allowing for ultra-fast filtering before the AI even begins its analysis.
Key Features of the Software
1. Intelligent Log Sync & Hybrid Chunking Pipeline
The core of the system’s high-precision retrieval is its specialized ingestion pipeline. Standard RAG systems use fixed-length chunking (e.g., every 1000 characters), which catastrophically breaks the context of software logs.
Decision: Request-Centric Semantic Grouping: I developed a custom "Request-First" chunking strategy. Instead of arbitrary splits, the system identifies the request_id within the JSON logs and groups all related activities (INFO, WARN, ERROR) into a single semantic unit.
Implementation:
Session Reconstruction: A Python-based parser groups logs by unique session IDs, ensuring the "entire story" of a transaction is sent to the vector database as one document.
Hybrid Fallback: For large-scale background processes that lack a Request ID, I implemented a 10-minute sliding time window to maintain temporal context.
Metadata Enrichment: Each chunk is tagged with singular and array-based fields (user_ids, lab_ids, services) for high-speed pre-filtering in PostgreSQL.
2. Agentic Multi-Agent QA System (RAG)
To meet the "Trust-But-Verify" requirement of healthcare, I replaced the traditional "one-shot" LLM response with a sophisticated Multi-Agent workflow using LangGraph.
Decision: Verification-First Orchestration:I architected a cyclic state machine where specialized agents collaborate to produce a verified answer, rather than a "best-guess" summary.
Implementation:
The Retrieval Agent: Acting as the "Librarian," this agent uses specialized tools to perform pgvector semantic searches and MySQL identity lookups (e.g., converting a User Name into a User ID found in logs).
The Summarization Agent: Analyzes the retrieved context to identify patterns, error sequences, and root causes, producing a draft response.
The Verification Agent: The "Quality Controller." This agent cross-checks the draft against the raw log documents. If it detects a claim not supported by the data (hallucination), it forces a correction before the user ever sees the message.
Real-Time Streaming: Leveraging Server-Sent Events (SSE), the entire multi-agent deliberation is streamed to the UI, providing the user with immediate visibility into the "Thinking Process."
Challenges Faced and Solutions
Problem 01: The "Silent Hang" & Latency in Multi-Agent Orchestration
During early testing, the system faced a critical performance bottleneck. Response times were exceeding 4 minutes, and frequently, the AI would "hang" indefinitely without returning an answer. This was unacceptable for a real-time log analysis tool where DevOps engineers need answers in seconds.
The Discovery: The issue was a deep technical conflict within the LangChain framework: combining native structured output (ProviderStrategy) with tool calls on the same model caused an internal processing loop that broke the streaming pipeline.
The Solution: I implemented a Hybrid Strategy Orchestration to bypass the framework limitations:
Critical Path Isolation: I restricted structured output only to the Retrieval Agent, which requires it for internal routing logic.
Plain-Text Optimization: I switched the Summarization and Verification agents to a high-speed plain-text configuration.
Regex Message Filtering: Since the Retrieval Agent now returned raw JSON in its stream, I developed a custom filtering layer on the backend to "clean" the JSON noise before it reached the user's screen.
Performance Gain: These architectural changes reduced the response time from 4+ minutes to under 12 seconds—a ~25x improvement in speed.
Problem 02: Recursive "Agentic Hallucination" Loops
When users asked ambiguous or open-ended questions like "Is anything wrong?", the Retrieval Agent would often fall into an "Infinite Tool Loop." It would call the retrieval tool repeatedly with slight variations, hoping to find "something" relevant, leading to high API costs and a frozen UI.
The Solution: I implemented a three-layered guardrail system to ensure agent reliability:
Strict Recursion Limits: I configured the LangGraph execution with a deterministic cap of 15 steps. If an agent fails to reach a conclusion within this limit, the system gracefully terminates the loop and provides a summary of what it found so far.
Context-Aware Prompt Engineering: I redesigned the system prompts with a "Minimal Search" protocol. The agent is explicitly instructed to review the conversation history first. If the history already contains the answer (e.g., resolving "the 13th" to "2026-01-13"), it is forbidden from calling the retrieval tool again.
Multi-turn "Stateful" Memory: By using a unified MemorySaver checkpointer, I ensured the agent maintains a historical "mental model" of the conversation, preventing it from searching for data it had already analyzed in previous turns.
Future Vision / next steps
Long-term vision
Predictive Anomalies: Moving from "Reactive" (searching logs after an error) to "Proactive"—using the RAG system to scan incoming logs in real-time and alert the team before a system crash occurs.
Interactive Trace Visualization: Adding a UI feature that allows users to click on an AI-generated answer to visually "jump" into the exact spot in the log file, creating a seamless bridge between natural language and raw data.



Get visibility from recruiters & peers
Build your portfolio & personal brand
Connect with like-minded developers
